Quantitative neuroimaging has become a cornerstone of precision medicine. NeuroQuant automatically transforms routine MRI scans into objective volumetric measurements, empowering clinicians to visualize, quantify, and track structural brain changes with reproducibility and confidence.
NeuroQuant provides standardized data that enhance clinical interpretation across a range of neurological conditions, including neurodegeneration, trauma, epilepsy, and developmental disorders. NeuroQuant’s 5 standard, disease-specific reports help drive precision in disease management by providing data on relevant structural volumes.
Dementia and Age-Related Atrophy Report: Tracking Neurodegeneration and Hippocampal Occupancy
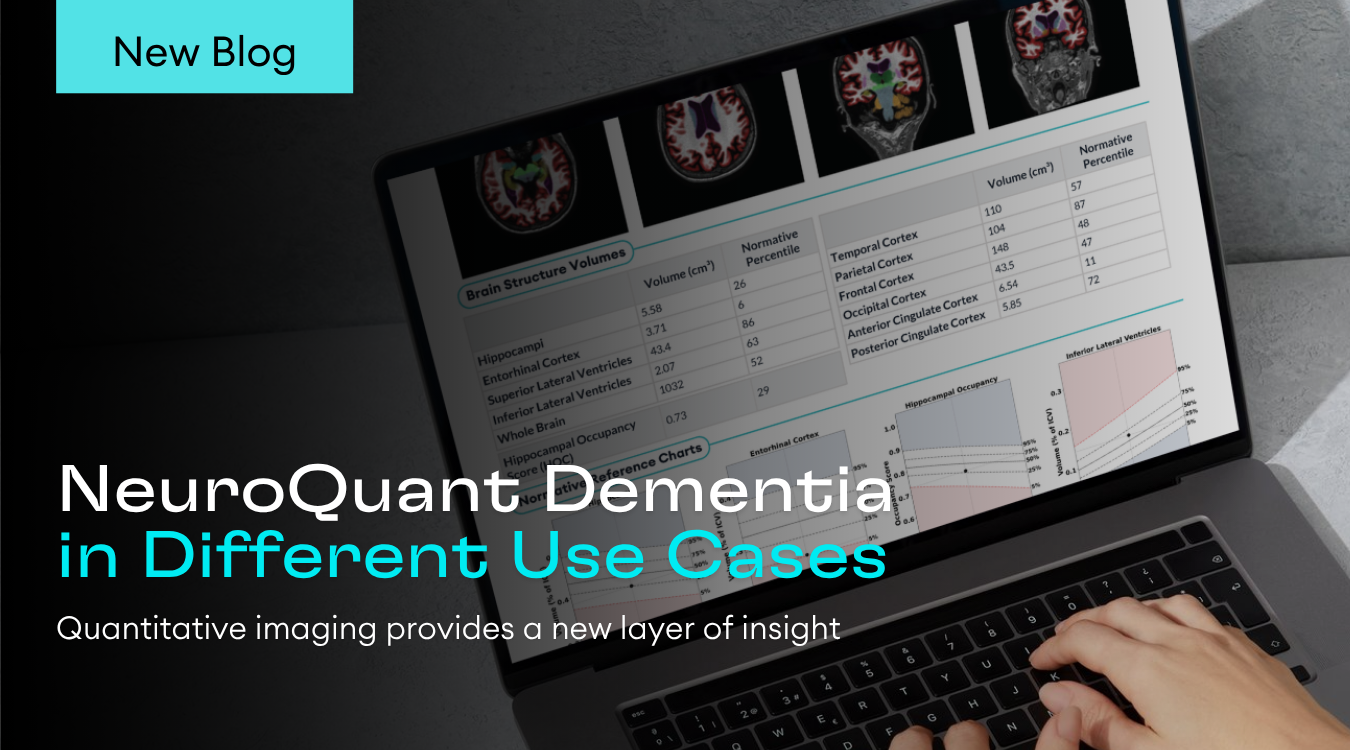
The NeuroQuant Dementia Report quantifies key brain structures involved in neurodegenerative disease, comparing volumes to an age‑ and sex‑matched normative database. Percentile rankings help identify deviations from expected ranges to provide insight into patient clinical condition.
The structures included in the Dementia Report include hippocampi, entorhinal cortex, superior and inferior lateral ventricles, whole brain, lobar cortices, anterior cingulate cortex, and posterior cingulate cortex. This report also includes hippocampal occupancy (HOC) score, an indicator of the balance between hippocampal and inferior lateral ventricle volumes, to help assess mesial temporal lobe atrophy often observed as a hallmark pattern of Alzheimer’s disease.
Key use cases:
- Early detection of hippocampal and temporal lobe atrophy in mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
- Support of differentiation between Alzheimer’s‑type, frontotemporal, and other atrophic patterns
- Longitudinal tracking of disease progression or treatment response
- Objective measurement for patient follow‑up and clinical trials
Multi‑Structure Atrophy Analysis: Beyond the Hippocampus
While hippocampal atrophy is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, multi‑structure atrophy can provide additional insight into other neurodegenerative syndromes. NeuroQuant Multi-Structure Atrophy (MSA) Report evaluates volumetric data across cortical and subcortical structures, allowing clinicians to visualize disease‑specific signatures.
The structures included on the MSA report include whole brain, cortical gray matter, cerebral white matter, hippocampi, thalami, superior and inferior later ventricles, and 3rd ventricle.
Key use cases:
- Atypical Parkinsonism
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- Multiple Sclerosis-related volume loss
- Subcortical atrophy
Total Brain Atrophy: Objective Evaluation After Injury
In traumatic brain injury (TBI), subtle diffuse atrophy can be difficult to visualize qualitatively. Total Brain Atrophy Report compares regional volumes to normative data to highlight structural changes resulting from injury. This comprehensive report contains data on 37 key structures.
Key use cases:
- Quantifying atrophy in frontal, temporal, or subcortical regions
- Assessing global patterns of abnormal percentile calculations
- Identifying right to left asymmetry
Pediatric Brain Development Report: Assessing Growth and Maturation
NeuroQuant’s Pediatric Report compares individual brain structure volumes to an age‑ and sex‑matched normative database from childhood through adolescence.
The structures included in the Pediatric Brain Development Report include whole brain, cerebral white matter, cortical gray matter, lobar cortices, cerebellum, and ventricles.
Key use cases:
- Evaluating developmental delays or macro/microcephaly
- Tracking structural maturation in conditions like autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or ADHD
- Quantifying volumetric differences in pediatric epilepsy or metabolic disorders
- Longitudinal follow‑up during neurodevelopmental intervention programs
Seizure and Hippocampal Asymmetry: Quantitative Epilepsy Assessment
In epilepsy and seizure disorders, hippocampal asymmetry is a critical biomarker that can influence surgical planning and diagnosis.
The NeuroQuant Seizure report quantifies right and left hippocampal volumes and assigns an asymmetry index to evaluate unilateral conditions.
Key use cases:
- Measuring unilateral hippocampal volume loss in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE)
- Establishing objective pre‑ and post‑surgical volumetric baselines
- Documenting hippocampal sclerosis progression in chronic epilepsy
Conclusion
NeuroQuant brings quantitative consistency to brain MRI, enabling clinicians to move beyond subjective impressions toward objective, data‑driven insights. From neurodegeneration and demyelination to pediatric development, trauma, and seizure disorders, its suite of reports supports better decision‑making, clearer communication, and longitudinal patient care.