One of the most frequently asked questions among Cortechs.ai customers is, “What does the Hippocampal Occupancy Score (HOC) represent within the NeuroQuant Dementia: Age-Related Atrophy report?”
The NeuroQuant Dementia: Age-Related Atrophy report presents volumetric information on brain structures relevant to Alzheimer’s disease and dementia, as well as their normative comparison to age and gender-matched reference data. The structures in this report include the hippocampus, superior and inferior lateral ventricles, entorhinal cortex, lobar cortices, anterior cingulate, and posterior cingulate. The clinical utility of this report lies in determining atrophic patterns that may be attributed to certain types of dementia. For example, preserved hippocampal volumes alongside reduced frontal and temporal lobe volumes may signify frontotemporal dementia. Diminished hippocampal volumes in the presence of statistically significant inferior lateral ventricle enlargement could indicate the presence of Alzheimer’s disease, when considering additional clinical factors.
The HOC score, as part of the NeuroQuant Dementia: Age-Related Atrophy report, takes dementia analysis a step further. The HOC score can help identify progression from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to Alzheimer’s disease.
What is the HOC score?
The HOC score is a calculated metric used to estimate mesial temporal lobe atrophy based on inferior lateral ventricle expansion.
Essentially, it is a ratio of the hippocampal volumes to the inferior lateral ventricle + hippocampal volumes:
HOC = Hippocampal Volume / (Hippocampal Volume + ILV Volume)
Since Alzheimer’s disease typically begins with hippocampal breakdown (responsible for memory loss) and compensatory inferior later ventricle expansion (ex-vacuo dilatation), a low HOC score can signify the likelihood of Alzheimer’s disease progression.
Where can I visualize the HOC score?
The HOC score is visualized in the Brain Structure Volumes Table in the Dementia: Age-Related Atrophy report. The HOC value is given in the “Volume” column, while the comparison to age and gender- matched norms is given in the “Normative Percentile” column.
Case Examples: Clinical Relevance of the HOC score
Case 1: 75-Year- Old Female
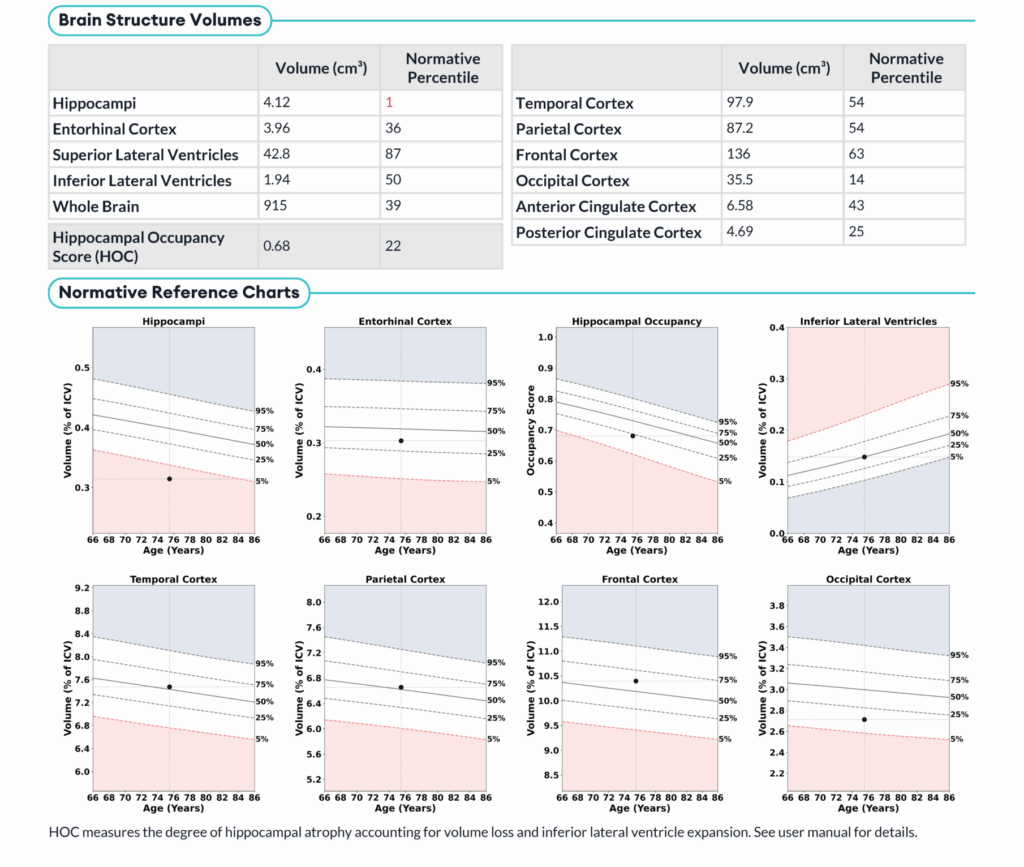
- HOC:68
- Volumetric Findings:
- Hippocampi:12cm3, 1st normative percentile
- ILV: 94cm3, 50th normative percentile
- Conclusion: Volumetric analysis does not support mesial temporal lobe atrophy with ex-vacuo dilatation. Possible congenitally small hippocampus.
Case 2: 58-Year Old Female
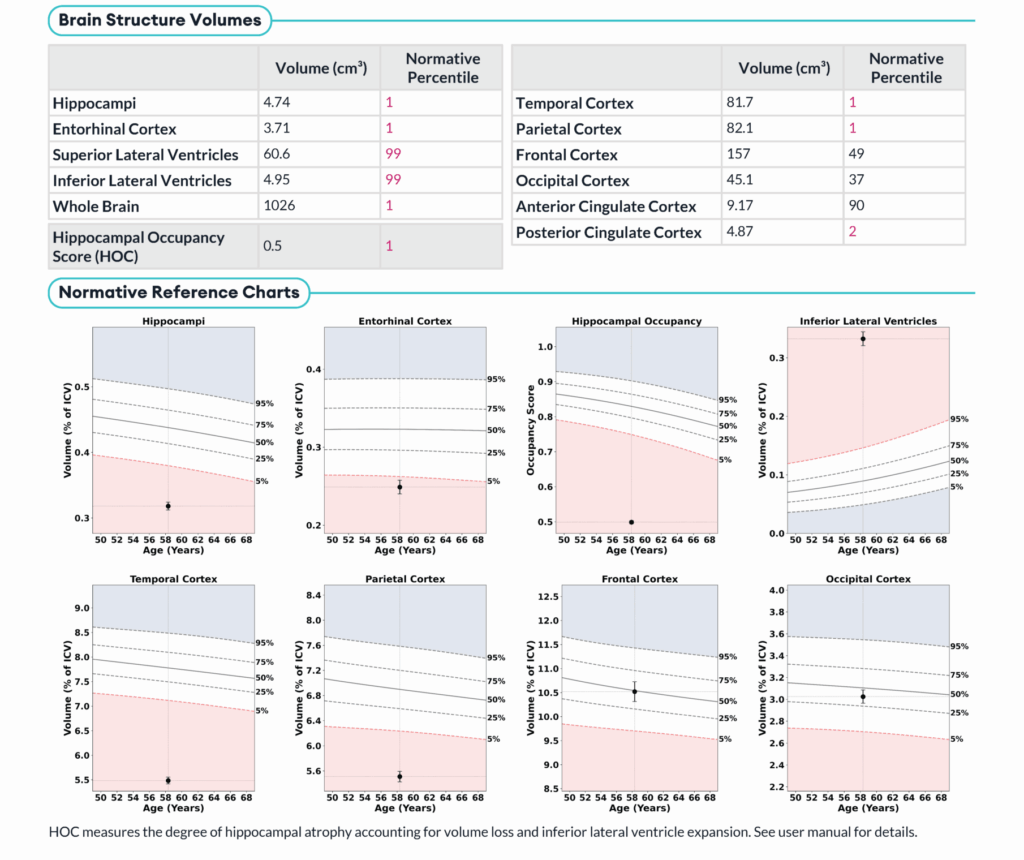
- HOC: 5
- Volumetric Findings:
- Hippocampi:75cm3, 1st normative percentile
- ILV:92cm3, 99th normative percentile
- Conclusion: Volumetric analysis demonstrates low normative volumes in the mesial temporal lobe with high normative volumes of the inferior lateral ventricles. This could signify ex vacuo dilatation consistent with Alzheimer’s disease progression.
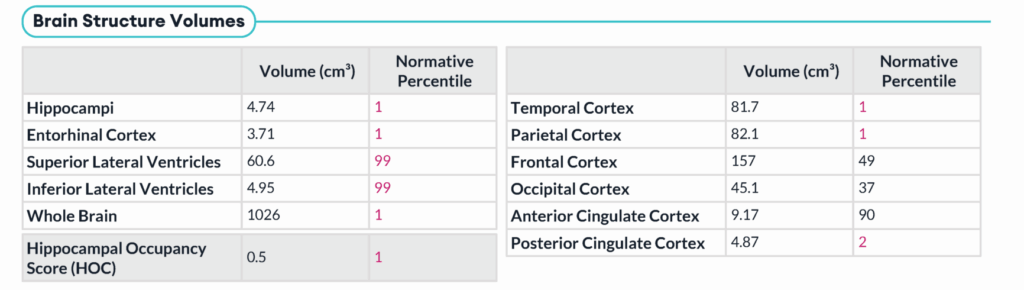
Case 3: 70-Year-Old Female
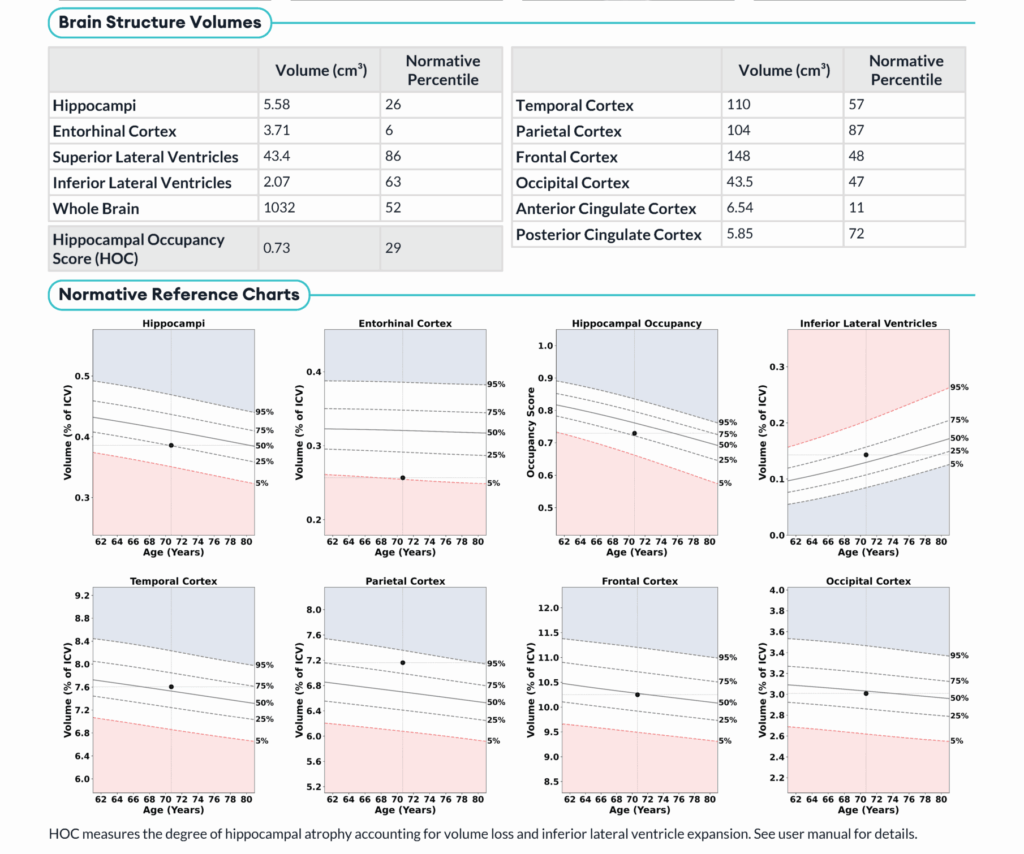
- HOC: 0.73
- Volumetric Findings:
- Hippocampi: 5.58cm3, 26th normative percentile
- ILV: 2.07cm3, 63rd normative percentile
- Conclusion: Volumetric analysis demonstrates hippocampal and inferior lateral ventricle volumes that are within normal limits for patient age and sex. No evidence of mesial temporal lobe atrophy.