In this post we discuss a case study detailing the importance of properly positioning and land marking the patient when performing a NeuroQuant® volumetric analysis.
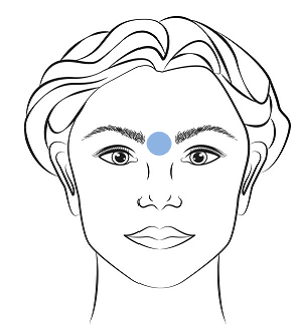 When positioning a patient on the MRI table, land marking the X, Y and Z coordinates in the glabellar region is critical (see image). Land marking the patient in this region of the head, specifically the area between the eyebrows and above the nose, allows the center of the brain to align with the isocenter of the magnetic field. Magnetic field inhomogeneties are at their smallest magnitudes in isocenter. Therefore, positioning the head away from the isocenter in the + or – direction will cause greater distortion introduced by gradient nonlinearity.
When positioning a patient on the MRI table, land marking the X, Y and Z coordinates in the glabellar region is critical (see image). Land marking the patient in this region of the head, specifically the area between the eyebrows and above the nose, allows the center of the brain to align with the isocenter of the magnetic field. Magnetic field inhomogeneties are at their smallest magnitudes in isocenter. Therefore, positioning the head away from the isocenter in the + or – direction will cause greater distortion introduced by gradient nonlinearity.
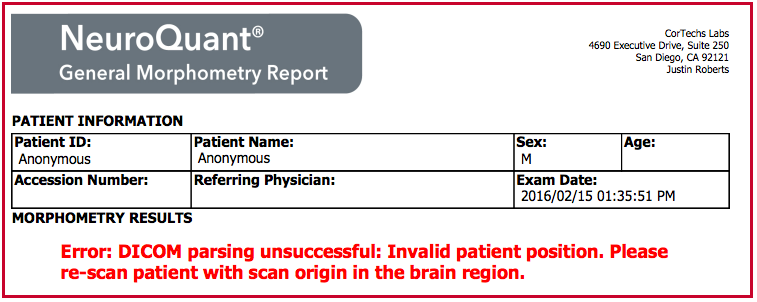
If a sequence is acquired and uploaded to NeuroQuant with any of the X, Y or Z coordinates outside +/-100mm, automated volumetric analysis cannot be performed. An error message will be returned to the queue monitor and/or PACS. Below is an example of the NeuroQuant error message that would be generated in this case.
Automated volumetric analysis is not possible in these instances. If NeuroQuant returns such an error message, re-scanning the patient with the scan origin centered appropriately is advisable.
Important note: If your patient is having an MRI performed on a body part other than the brain (i.e. cervical, thoracic, lumbar spine) it is very important to re-establish the glabellar region of the head as isocenter prior to acquiring the NeuroQuant volumetric scan.
Interested in learning more about how to ensure accurate NeuroQuant output results?
- Explore the importance of using a 3D T1 sagittal MRI sequences for NeuroQuant analysis. You can read that blog post here.
- Review how to ensure accurate NeuroQuant processing results. You can read that blog post here.
- Understand why contrast agents are not used to achieve quality segmentation with NeuroQuant. You can read that blog post here.
- Examine why good alignment to atlas is necessary. You can read that blog post here.
Additionally, more information about using and processing NeuroQuant can be found here.
References:
- Caramanos Z. et al. Gradient distortions in MRI: characterizing and correcting for their effects on SIENNA-generated measure of brain volume change. Neuroimage, 2010, Jan15:49(2):1601-11.
- Velthuizen R. et al. Review and evaluation of MRI nonuniformity for brain tumor response measurements. Med. phys. 25, 1655(1998).
![]()