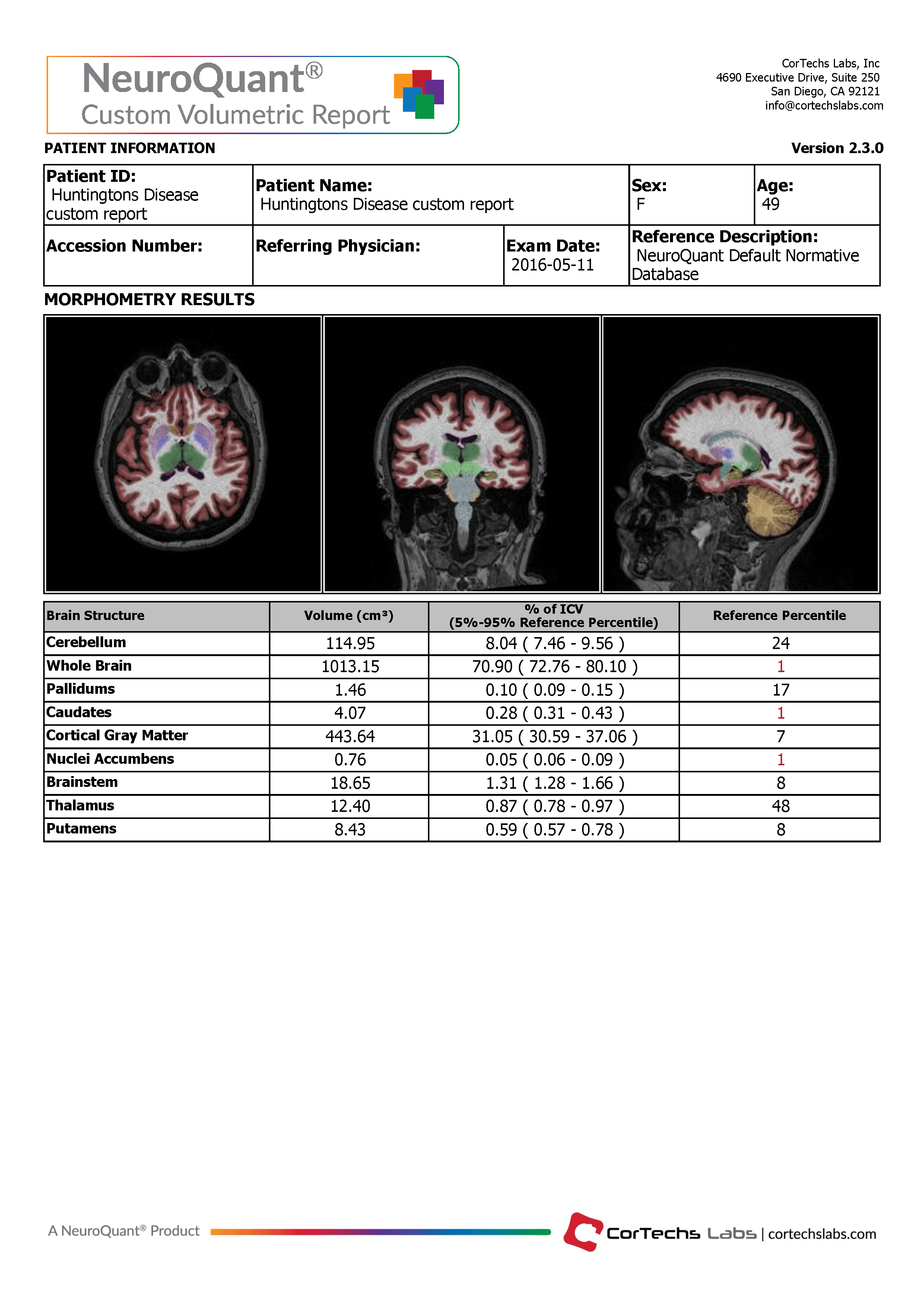
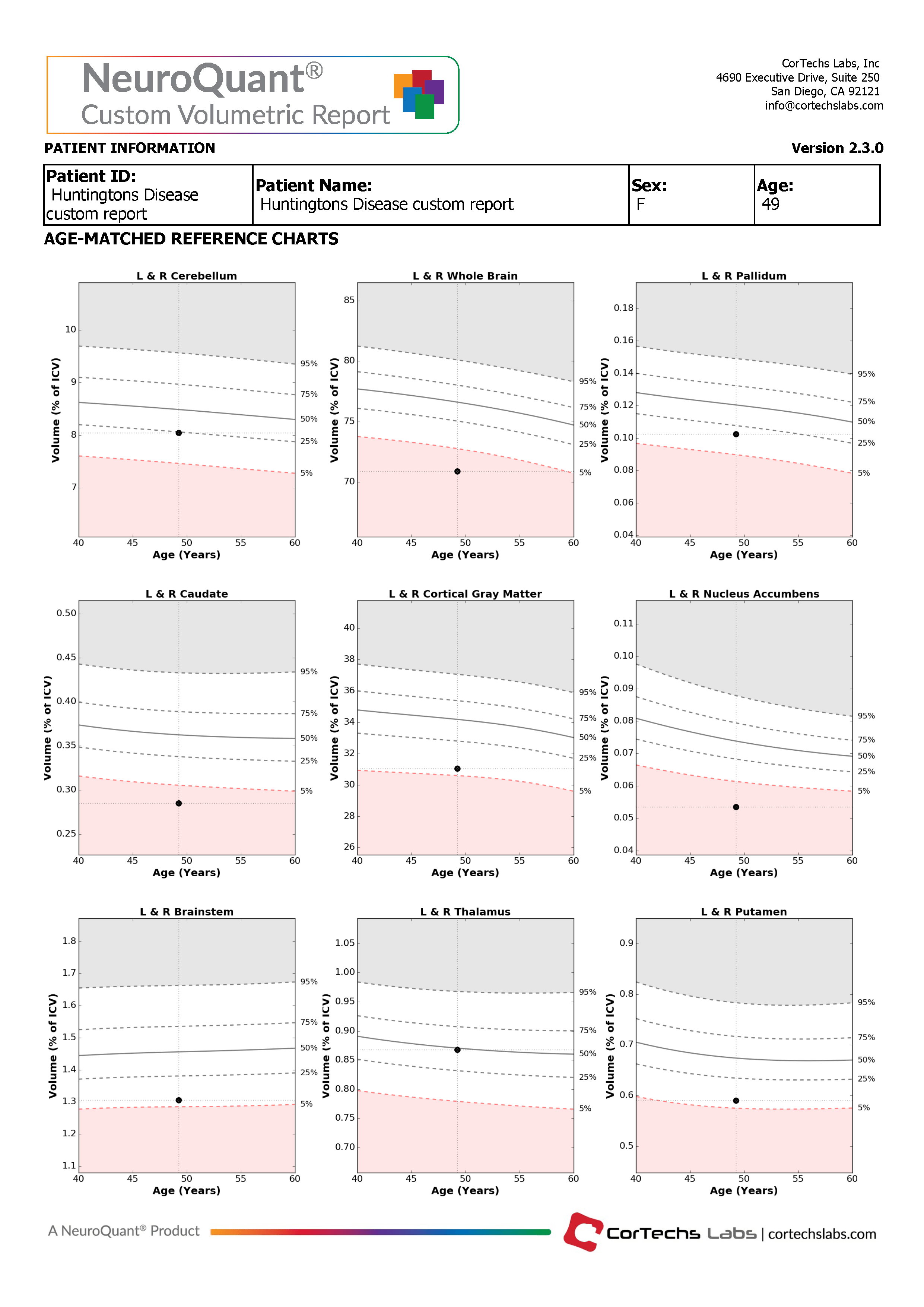
Automated volumetric MR imaging provides an opportunity to extend brain structure volume measurements to monitor and assess disease progression and drug therapy efficacy for patients with Huntington’s Disease (HD) by showing regional and whole brain atrophy, that can be tracked and evaluated over time.
In patients with HD, whole brain volume loss, especially within gray matter structures, has been correlated with HD progression. Specifically, the main components of the basal ganglia – caudate, putamen, nucleus accumbens, pallidum, as well as strongly connected structures – cerebellum, thalamus and brainstem, have been correlated with disability progression and cognitive impairment. According to several studies, structural volume measurements provide applicable biomarkers for evaluating HD therapies.
For clinicians looking to evaluate HD and HD drug therapies with volumetric MR imaging, we recommend using the NeuroQuant Custom Volumetric report, which provides volume measurements for up to nine clinician-selected brain structures relevant to HD. Additionally, the clinician is able to review axial, coronal and sagittal image sets with the segmented brain structures each given a different color, directly in PACS or a DICOM viewer.
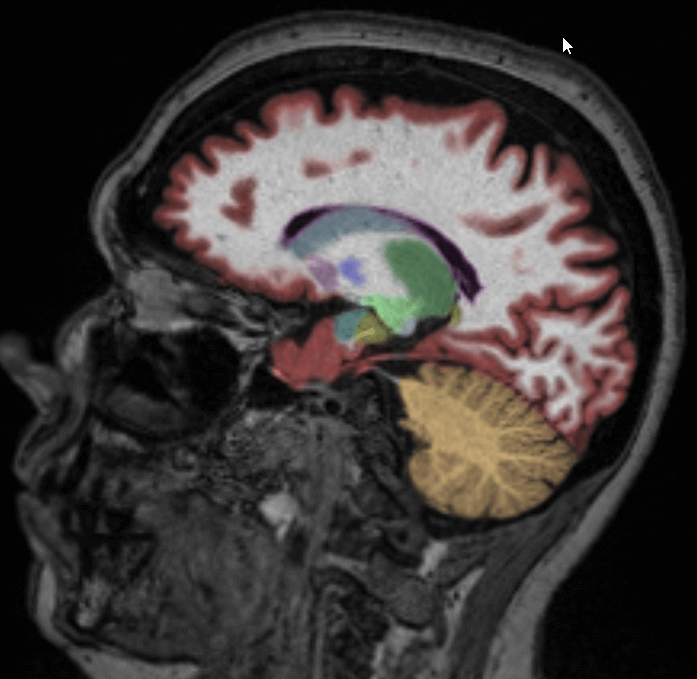
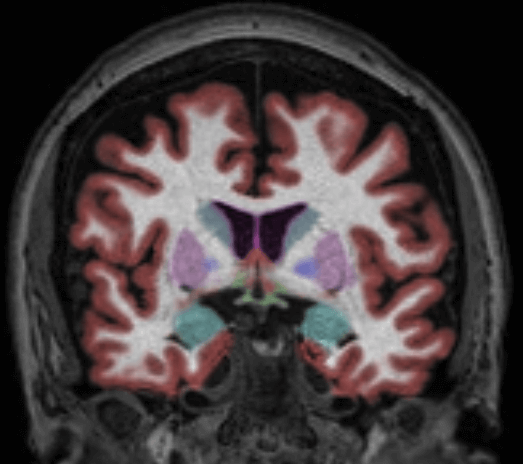
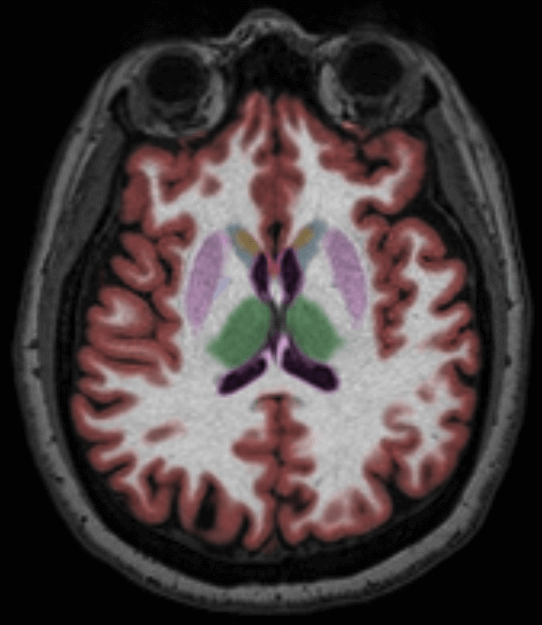
The Custom Volumetric report indicates the patient’s brain structure volume measurements as compared to a healthy population via Cortechs.ai’ normative reference data. This allows NeuroQuant to deliver a precise indication of where that individual’s brain structure volumes lie within an age- and gender-based reference chart.
The NeuroQuant Custom Volumetric report provides a multi time point feature, which can be used to assess volume changes over time by displaying the results of follow up measurements together with all previous measurements, on the same report. Physicians can use this information to quickly and easily evaluate longitudinal change in several global and subcortical brain structures.
Majid D.S.A., et al. (2011) Basal Ganglia Atrophy in Prodromal Huntington’s Disease is Detectable Over One Year Using Automated Segmentation. Movement Disorders. 26(14): 2544-2551
Niccolini, F. (2014) Neuroimaging in Huntington’s Disease. World J Radiol 6(6): 301-312