No two brain injuries are ever the same. Just ask any physician who routinely examines and treats them. Brain trauma occurs when foreign objects pierce the skull or a person experiences a severe fall or blow to the head causing the brain tissue to be bruised or torn. Because brain injuries happen in different ways, treatment is dynamic and based on many factors including how the injury occurred, the patients age at injury, and medical conditions prior to the injury.
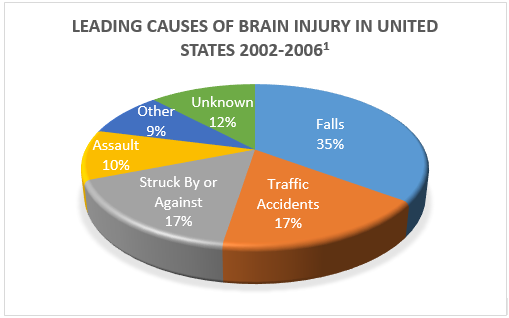
According to findings presented by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), from 2002-2006, falls and traffic accidents are the leading causes of brain injuries. The highest rates of falls were for children (ages 0-4) and adults (ages 75 and older). Adults ages 20-24 were more likely to encounter brain injuries from motor vehicle accidents.
This graphic doesn’t include military personnel where a common combat-related injury is closed head trauma (a brain injury where the skull is not fractured), whose signs and symptoms of brain trauma are not immediately apparent2 or where it is difficult to discern effects of brain trauma from other conditions such as PTSD or depression.
A new report provided by Cortechs.ai is the NeuroQuant Triage Brain Atrophy Report, which can be used by physicians in the assessment of brain trauma. NeuroQuant works by segmenting and measuring brain structure volumes based on MRI images and compares the brain volumes to a normative database. The Triage Brain Atrophy report is available for ages 3 to 100 and provides neurologists and radiologists volume measurements of 39 brain structures separated in right and left hemisphere and sorted by lobe and region – a powerful tool in providing objective evidence of changes to brain anatomy after injury.
- Faul, M., Xu, L., Wald, M.M., Coronado, V.G. (2010). Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths 2002–2006. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control
- The Brain Trauma Foundation. https://www.braintrauma.org/tbi-faqs/military-tbi/