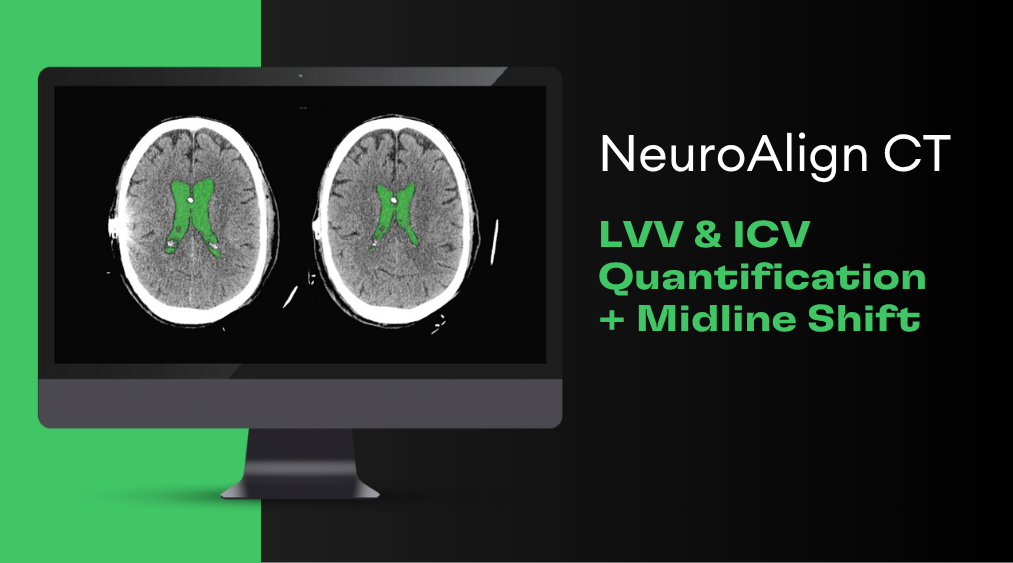
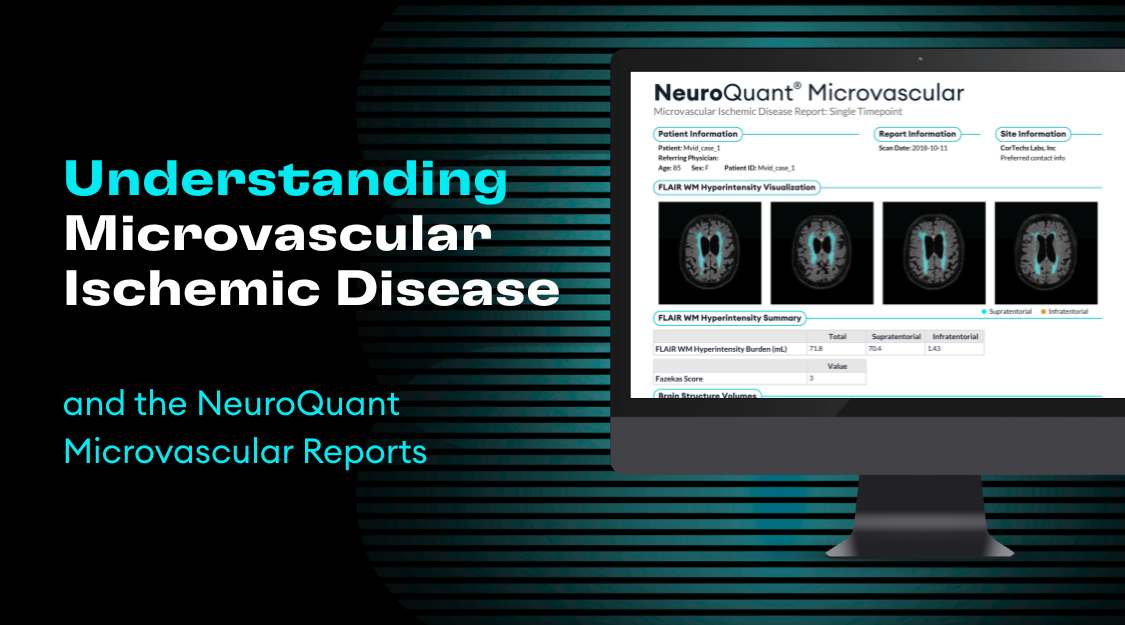
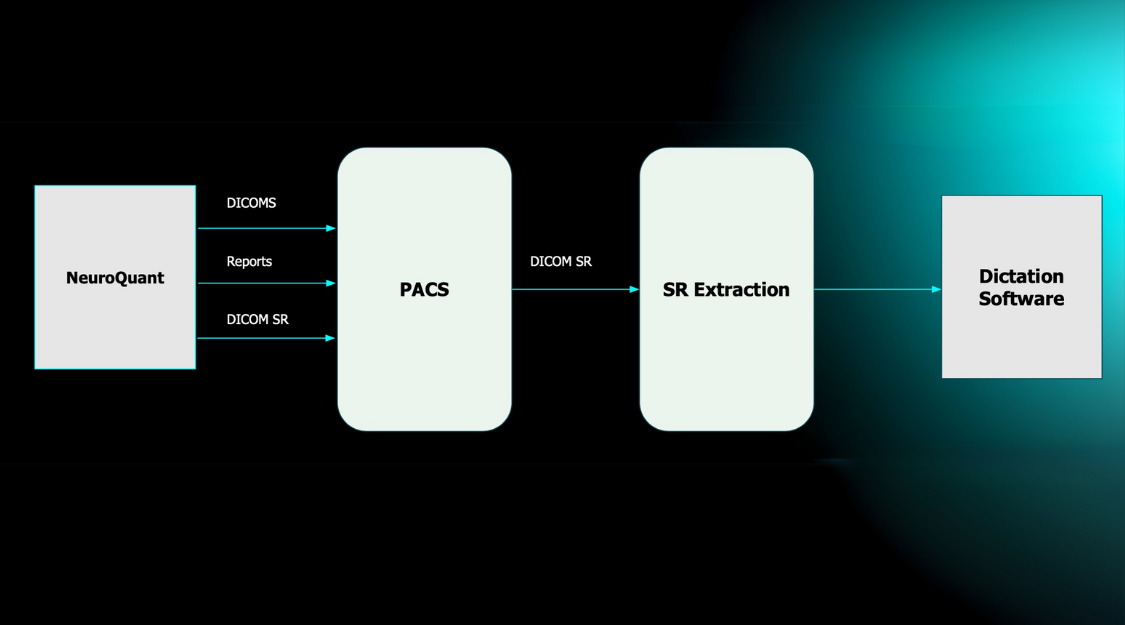
Cortechs.ai is providing the most widely used clinical brain morphometry tool to help with the follow-up of COVID-19 patients and to contribute to neurological research of the pandemic.
As the COVID-19 pandemic progresses, there are reports from different institutions around the world of neurological symptoms and manifestations in the central and peripheral nervous systems (CNS, PNS). Due to these findings, Cortechs.ai is offering a new complimentary brain volumetric report package.
Our LesionQuant FLAIR Lesion Report, NeuroQuant Triage Brain Atrophy (TBA) and Custom COVID-19 reports (learn more) are available, free of charge, to all facilities for COVID-19 patients or for COVID-19 research. Through the use of our automated software, it is possible to monitor the volumes of 75 brain structures and regions, as well as any changes in lesion burden or lesion distribution over time. As the research on the neurological effects of the disease is ongoing, our offering may be updated accordingly.
Neurological and Respiratory ConnectionLi and colleagues at Jilin University believe that SARS-CoV-2 may infect nerve cells, particularly neurons in the medulla oblongata, which is part of the brain stem that serves as the control center for the heart and the lungs, the damage could contribute to “acute respiratory failure of patients with COVID-19.” Their autopsy studies demonstrated that signs of cerebral edema and meningeal vasodilation could be detected in most cases of SARS.
Since the World Health Organization (WHO) [1] published the first technical publication for the scientific and public health community, and world media, on January 5, 2020, the clinical focus has primarily centered on the virus’ prodromal symptoms and severe respiratory effects. However, many neurologists are now reporting that COVID-19 symptoms may also include encephalopathy, ataxia, and other neurologic signs. A study published in the Journal of Medical Virology [2], Li, Bai, and Hashikaw (2020) stated that “increasing evidence shows that coronaviruses are not always confined to the respiratory tract and that they may also invade the central nervous system, inducing neurological diseases.”
Central Nervous System, Peripheral Nervous System, and Skeletal Muscular Manifestations
While COVID-19 primarily affects the lungs, the latest research (below) shows that patients, especially ones with more severe infection, may also manifest neurologic symptoms of the CNS, PNS, and skeletal muscular symptoms. Cortechs.ai’ existing fully automated brain volumetric solutions can be easily customized to provide COVID-19 relevant brain volumetric information in minutes.
COVID-19 patients may manifest neurologic symptoms, which, according to Mao et al. (2020) in an article published in JAMA Neurology [3], are more likely to manifest in patients with more severe infection. In this study, 36.4% of patients experienced:
CNS Symptoms:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Impaired consciousness
- Acute cerebrovascular disease
- Ataxia
- Seizures
PNS Symptoms:
- Taste impairment
- Smell impairment
- Vision impairment
- Nerve pain
Mao and colleagues found that some patients develop COVID-19-related symptoms only after showing neurologic symptoms, but the rate of neurological symptoms is higher in patients with more severe respiratory disease status1. According to Kandemirli et al. (2020) in a study published by the Radiological Society of North America [4], of those patients in the intensive care unit with COVID-19 infection presenting neurologic symptoms who underwent MRI, 44% (12/27) had abnormal MRI findings.
While Cortechs.ai’ NeuroQuant and LesionQuant volumetric software were not designed to diagnose COVID-19, they can provide longitudinal quantitative data to inform clinicians about brain regions the disease could be affecting and automatically compare the results with others of the same age and sex. This may help physicians detect and address any findings that are treatable.
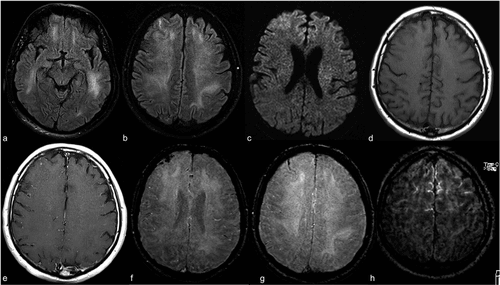
The MRI images here demonstrate an exam of a 59-year old intubated male patient with altered mental status. The FLAIR images demonstrate prominent symmetric white matter hyperintensity and right frontal cortical hyperintensity. There is also linear hyperintensity within the frontal sulci. These hyperintensities will be automatically quantified and tracked longitudinally with LesionQuant.
Complimentary COVID-19 Report Package
The LesionQuant FLAIR Lesion Report, NeuroQuant Triage Brain Atrophy (TBA) and Custom COVID-19 reports are available in a complimentary package. These reports segment and quantify patient brain structures and lesions in under 30 minutes. As the research on the neurological effects of the disease is ongoing, our offering may be updated accordingly.
This complimentary report package is intended to be used in the follow-up of patients who have been diagnosed with COVID-19 and are experiencing neurological symptoms.
References
- WHO Timeline – COVID-19. (2020). Retrieved 28 May 2020, from https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-04-2020-who-timeline—covid-19
- Li YC, Bai WZ, Hashikawa T. The neuroinvasive potential of SARS-CoV2 may play a role in the respiratory failure of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. February 27 2020:10.1002/jmv.25728. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25728. Epub ahead of print.
- Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. Published online April 10, 2020. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127
- Kandemirli, Sedat G et al. “Brain MRI Findings in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with COVID-19 Infection.” Radiology, 201697. May 8, 2020, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201697